Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC, 2004
April, 2004 − Rev. 1
1 Publication Order Number:
AN1080/D
AN1080/D
External−Sync Power
Supply with Universal Input
Voltage Range for Monitors
Prepared by: S.K. Tong and K.T. Cheng
ABSTRACT
This paper describes the design of a low−cost 90 W
flyback switching power supply for a multi−sync color
monitor. In order to minimize the screen interference from
the switching noise, the power supply can be automatically
synchronized at the fixed frequency of the horizontal
scanning frequency (15 to 32 kHz) of the color monitor. The
line and load regulations of the power supply are excellent.
Also, a new universal input−voltage adaptor enables the
power supply to operate at two input voltage ranges, 90−130
Vac or 180−260 Vac. It can minimize the ripple current
requirement of the input bulk capacitors and the stresses on
the power switch. The design demonstrates how to use
recently introduced components in a low−cost power
supply. The state−of−the−art perforated emitter
epi−collector bipolar power transistor MJE18004 and
opto−isolator MOC8102 are utilized.
1. INTRODUCTION
As the resolution of modern color display increases, the
power supply for these high−definition monitors become
critical in its features and performance. Nowadays,
switching power supplies replace the linear regulators
due to high efficiency and light weight. However, the
EMI/RFI generated by switching power supplies has
adverse effects on the resolution of high−definition color
monitors (e.g. 800 x 600 or higher). Asynchronous
switching noise beat with the horizontal scanning frequency
of the color monitor, creating undesirable interferences and
jitter on the screen. It affects the horizontal resolution of the
high−definition color monitor because the random pulses
generated by the asynchronous switching operation and also
deflect the electron beams and blur their precisely controlled
positions. Thus, the switching power supply for the
high−definition monitors or TVs must be synchronous with
the horizontal frequency.
Recently, multi−sync color monitors became popular
because they can adapt to several modes of computer
displays. For example, CGA, EGA and VGA display modes
are used in IBM PCs. The three display modes have different
horizontal resolutions and scanning frequencies, ranging
from 15.7 kHz to 31.5 kHz. Hence, the switching power
supply developed in this note can be synchronized to the
horizontal scanning frequencies of the multi−sync color
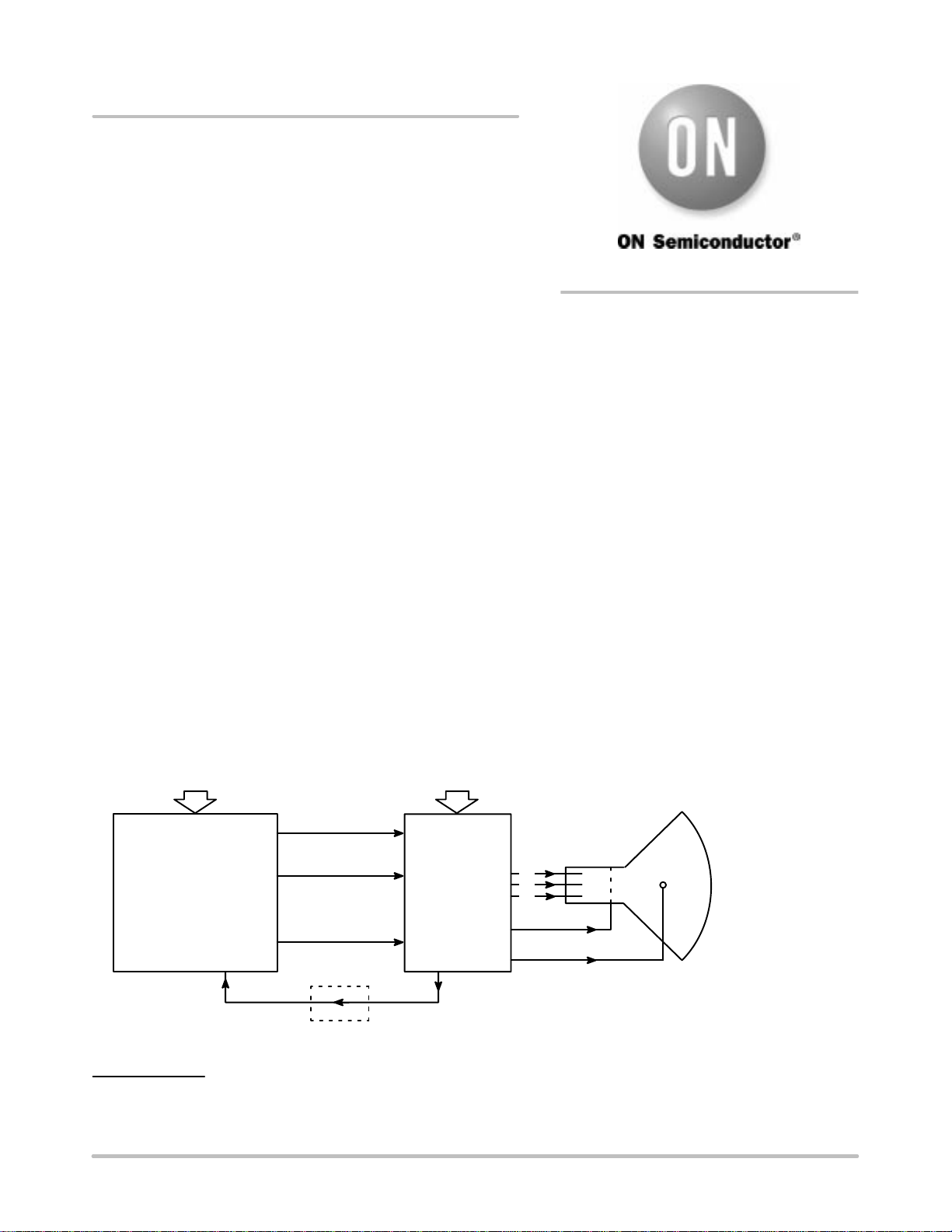
monitor, as shown in Figure 1. It provides three DC outputs.
The specifications are:
Figure 1. Block Diagram of Modern Multi−Sync Color Monitor
AC LINE
MULTI−SYNC SIGNALS FROM COMPUTER (H & V SYNC, RGB SIGNALS)
MULTI−SYNC
VIDEO
PROCESSOR,
RGB DRIVERS
& HV CIRCUIT
(FOR LOGIC ICs)
POWER SUPPLY
DEVELOPED IN
THIS NOTE.
+5 V
(AUX. POWER)
+12 V
(MAIN POWER)
−110 V
EXT. SYNC
H. SYNC
DC ISOLATION
R
G
B
HV
HIGH RESOLUTION
MULTI−SYNC
COLOR DISPLAY
FOCUS
HV
This document may contain references to devices which are
no longer offered. Please contact your ON Semiconductor
representative for information on possible replacement devices.
APPLICATION NOTE
http://onsemi.com
Verzeichnis








