herunterladen

Keywords:
negative voltage, synchronous step-down converter, inverting buck-boost, factory automation, industrial process control
APPLICATION NOTE 5775
HOW TO USE THE MAX17501 AND MAX17502 FOR NEGATIVE
OUTPUT VOLTAGE APPLICATIONS
By:
Dipankar Mitra
© Apr 30, 2014, Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
Abstract: This article shows how to produce negative output voltages from positive input voltages using the MAX17501 and MAX17502 synchronous
step-down converters.
Introduction
Industrial control equipment such as programmable logic controllers, I/O modules, mass flow controllers, and various other sensors and supporting
systems use analog components like amplifiers and multiplexers that operate on negative supply voltage. Typically operating at ±12V, ±18V or other
variations, these voltages are generated from a 24V DC bus. Maxim’s portfolio of high-voltage synchronous buck regulators offer 50% lower power
loss allowing customers to operate their equipment 50% cooler. In this application note, we discuss techniques to use these synchronous buck
regulators to generate negative voltages.
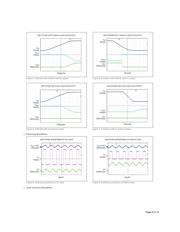
Design Considerations
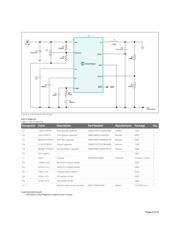
Synchronous buck converters can be configured to work in a buck-boost topology to produce negative output voltage from positive input voltage. This
application note explains how the
MAX17501 and MAX17502 synchronous step-down converters can be used to generate negative output voltage
from positive input voltage. A -15V output voltage application is used to demonstrate the principle.
Table 1. Negative Output Voltage Power-Supply Requirements
V Operating input voltage 24V ±6V
V Output voltage -15V
I Maximum output current 500mA
V Steady-state input ripple voltage 1% of nominal V
V Steady-state output ripple voltage 1% of nominal V
Operating Input Voltage Range
The sum of the maximum operating input voltage for the negative output application and the absolute value of the output voltage should not exceed
the maximum operating voltage (60V) of the MAX17501 and MAX17502, as expressed by the following equation:
V
+ |V | ² 60V
Therefore, for -15V output voltage, maximum operating input voltage can be as high as 45V. The minimum operating input voltage for the negative
output voltage application should be greater than 4.5V.
Calculating Duty Ratio
The expression for the duty ratio of the negative output power supply is shown below; ignoring the losses associated with the power switches and the
inductor DC resistance:
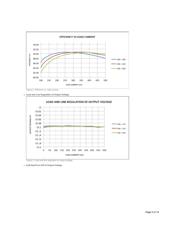
For the specifications listed above, the duty cycle varies between 0.45 at 18V input voltage to 0.33 at 30V input voltage. At the nominal input voltage of
24V, duty cycle is 0.38. Note that the highest duty ratio (D
) occurs at the minimum operating input voltage and the lowest duty ratio (D ) occurs
at the maximum operating input voltage (V
).
IN
OUT
OUT
IN_ripple IN
OUT_ripple OUT
IN_MAX OUT
MAX MIN
IN_MAX
Page 1 of 14
Verzeichnis
- ・ Blockdiagramm on Seite 3 Seite 4
- ・ Anwendungsbereich on Seite 1 Seite 2