herunterladen
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Interface Circuits > APP 578
Keywords: RS-485, rs485, tranceivers, EIA-TIA-485, 15kV ESD protected, fail safe, high common-mode
voltage, high CMR, fault detection, motor control, optical encoder, high-reliability, ESD protection
APPLICATION NOTE 578
New RS-485 IC Increases System Reliability and
Fault Detection in Motor-Control Circuits
Apr 01, 2001
Abstract: Applying a unique 3-channel RS-485 transceiver displaying many unusual features increases
reliability and fault-detection in motor-control applications. Designed specifically for motor shaft encoder
applications, the MAX3097 and MAX3098 feature three differential channels to handle optical encoder
data, ±15kV ESD protection, increased common mode rejection to -10 and +13.2V, three separate fault-
alarm flags, and fail safe open and short detection. Alarm flags indicate open or shorted line conditions,
excessive common-mode voltage range, and low-signal strength.
Modern factories use large electric motors to control machines that are necessary for the operation of
the plant. For increased flexibility and accuracy, these electric motors are sometimes processor-
controlled. It is imperative that the electronics controlling these large motors are designed in such a way
that, if a problem occurs, the motor is safely and quickly shut down. Failure to detect a problem and to
sufficiently control the motor can result in the destruction of expensive equipment, as well as in injury or
possibly even death. The MAX3097E/MAX3098E were specifically designed to be used with motors in
absolute positioning control loops. These parts have unique features which enable a safer and more
robust design in harsh industrial environments. To better understand the unique features of the
MAX3097E/MAX3098E, let's first review the basics of motor control.
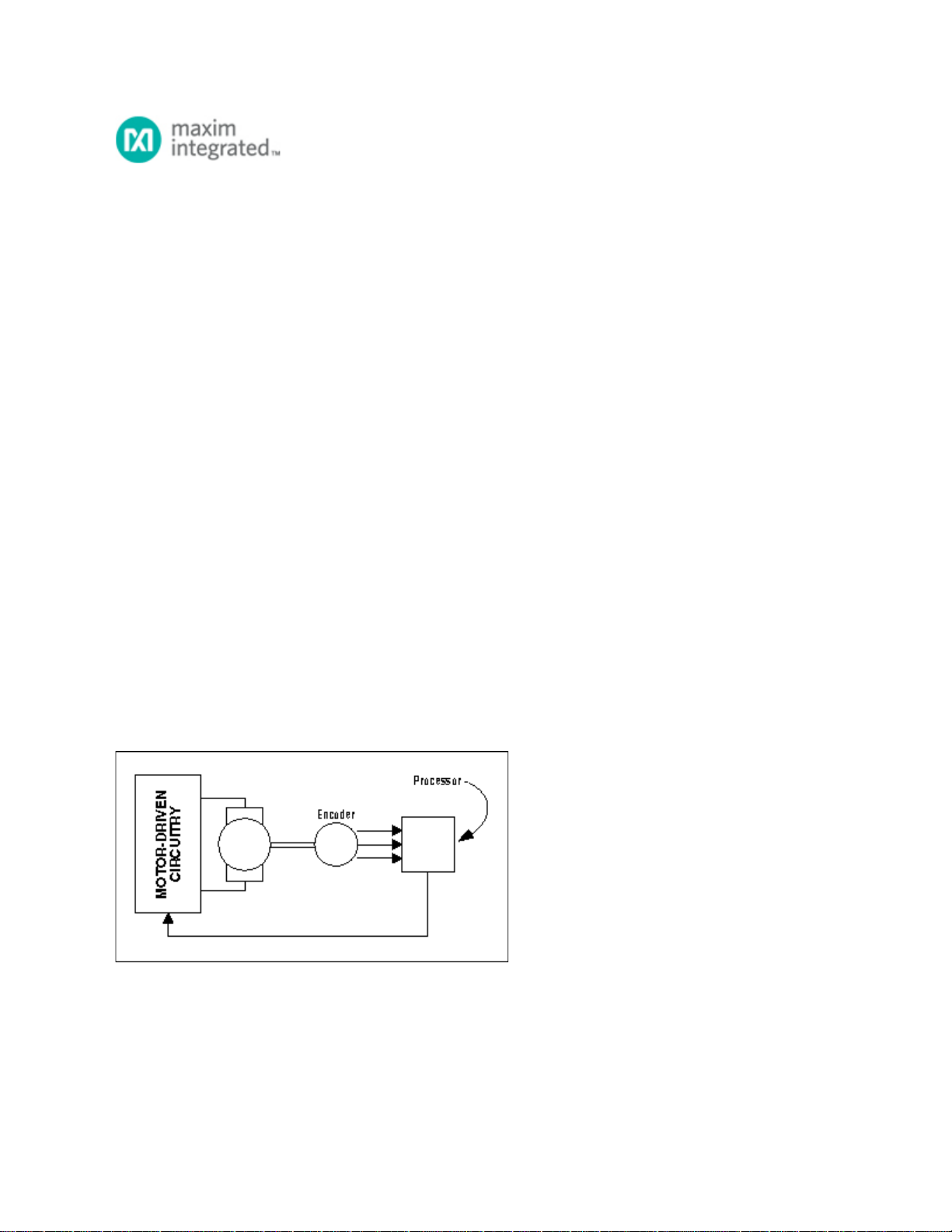
Figure 1. The major building blocks of processor-controlled electric motors.
The blocks in Figure 1 include a processor, motor-drive circuitry, an electric motor, and an encoder. The
processor decides how hard and where the motor should be driven. The motor-drive circuitry contains all
the necessary power electronics to drive the motor and the encoder provides position, direction, and
velocity information to the processor, thus closing the loop. To understand the operation of the
MAX3097E/MAX3098E, it is necessary to have a good grasp of the operation of the encoder.
Page 1 of 7