herunterladen
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Battery Management > APP 4936
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Digital Potentiometers > APP 4936
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Power-Supply Circuits > APP 4936
Keywords: power supply, calibrate, calibration, voltage reference, digital potentiometer, digipot,
mechanical potentiometer, resistive feedback
APPLICATION NOTE 4936
Calibrating a Power Supply with a Digital
Potentiometer
By: David Fry, Strategic Applications Engineering Manager
Apr 20, 2012
Abstract: A resistive feedback network is often used to set the output voltage of a power supply. A
mechanical potentiometer (pot) conveniently solves the problem of adjusting a power supply. For easier
automatic calibration, a mechanical pot can be replaced with a digital pot. This application note presents
a calibration solution that uses a digital pot, because digipots are smaller, do not move with age or
vibration, and can be recalibrated remotely. This proposed solution reduces the susceptibility of the
system to the tolerance of the digital pot's end-to-end resistance, making the solution optimal for
designers. This application note also explains some of the equations required to calculate the resistor
chain values and to use a digital pot in this way. A spreadsheet with standard reisistor values is available
for easy calculations.
A similar version of this article appeared on Power Management DesignLine, February 2012.
Introduction
A resistive feedback network is often used to set the output voltage of a power supply, since fixed
resistors are simple to use and low cost. However, because a fixed network is not adjustable, the output
voltage cannot be accurately set. Therefore, many power supplies use a mechanical potentiometer (pot)
in the feedback network to set the output voltage. For easier automatic calibration, a mechanical
potentiometer can be replaced with a digital potentiometer. Digital potentiometers are smaller, do not
move significantly with age or vibration, and can even be recalibrated remotely. This application note
explains some of the calculations required to use a digital potentiometer in this way and also provides a
spreadsheet for easy calculations.
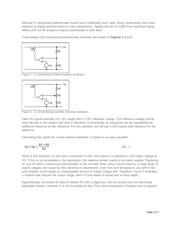
Conventional Power-Supply Feedback
A power supply often uses resistive feedback to set the output level. However, because there are many
device tolerances that can affect the output voltage, a fixed resistor-divider is often insufficient. In these
situations, a variable-resistor ratio is used so the system can be calibrated in final testing.
Page 1 of 7