herunterladen

Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Hot-Swap and Power Switching Circuits > APP 4906
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Power-Supply Circuits > APP 4906
Keywords: current, calibration, hot-swap, ADC, load, hot-plug, controller, MOSFET
APPLICATION NOTE 4906
Hot-Swap Controller with Calibration Input Can
Accurately Monitor Two Load Currents
By: Dwight Larson, Senior Member of the Technical Staff
Jan 20, 2011
Abstract: This application note describes how to employ the MAX5977 hot-swap controller and a single ADC to allow
precision, independent monitoring of load current in two domains: a high-power primary domain and a low-power
housekeeping domain. A MAX5976 integrated-MOSFET power switch can be used to provide simple, cost-effective
control of power to the housekeeping domain. Even though the monitoring function for both domains is combined in
the MAX5977, the protection and control of the two domains remains completely independent, which improves
reliability and safety.
Introduction
When a storage, processing, or network interface card is designed to be serviced or replaced in a high-availability
(always-on) system, a hot-swap or hot-plug controller must be used. This hot-swap circuit controls the turn-on and
turn-off of power to the card when it is inserted and removed from the system. It also protects the system against
overcurrent in the event of a fault on the load card. More sophisticated hot-swap controllers now include features
that allow monitoring of load voltage and current, which can in turn be used to calculate load power. This information
is extremely useful for optimizing efficiency, cooling, and allocation of limited power-supply output.
When load cards become larger and more complex, it is a good idea to split the power to the card into two or more
domains, where one domain is a "housekeeping" supply with lower power requirements, and the other domain
supplies the main power to the card. This approach allows the housekeeping supply to come up first and shut down
last for management purposes, while the high-power domain is controlled separately. However, if power monitoring
or metering is required, splitting the power into two domains usually requires use of two single-channel hot-swap
controllers (or at least a two-channel controller) to allow measurement of power for both domains.
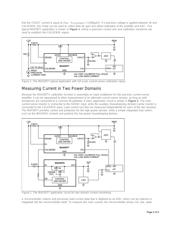
This application note describes how to employ the MAX5977 hot-swap controller and a single ADC to allow
precision, independent monitoring of load current in both domains, while a MAX5976 integrated-MOSFET power
switch provides simple, cost-effective control of power to the housekeeping domain.
MAX5977 Calibration Function
Maxim's MAX5977 performs the usual functions of a hot-swap controller, driving a high-side n-channel MOSFET
switch to control turn-on voltage slew rate and to protect against overcurrent conditions. In addition, the MAX5977
also includes a precision current-sense transconductance amplifier with a gain of 2500µA/V that can be used to feed
an external ADC for load current monitoring. To allow for precision calibration of the current-sense system, the
MAX5977 can switch its transconductance amplifier's inputs to an alternate "calibration sense" input. This feature is
controlled by the CAL input.
When CAL is logic low, the current-sense amplifier senses the voltage between IN and SENSE, so that a current
equivalent to (V
IN
- V
SENSE
) × 2500µA/V is output at CSOUT for current monitoring during normal operation.
However, if CAL is driven high, the MAX5977 switches the current-sense amplifier negative input to CALSENSE, so
Page 1 of 5