herunterladen
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Amplifier and Comparator Circuits > APP 484
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Battery Management > APP 484
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Miscellaneous Circuits > APP 484
Keywords: battery charger, solar power, MAX856, MAX982, boost converter, DC-DC converters, voltage
detector, solar cell, NiCd, NiMH batteries, dual comparator
APPLICATION NOTE 484
Harnessing Solar Power with Smart Power-
Conversion Techniques
Dec 01, 2000
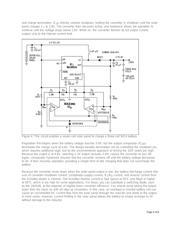
Abstract: Charge NiCd or NiMH batteries with solar cells. This circuit extracts the maximum power from a
solar array to charge a battery stack. It employs the MAX856 boost converter and MAX982 dual
comparator with reference.
Additional Information:
Quick View Data Sheet for the MAX856
Quick View Data Sheet for the MAX982
Samples and Literature Order Form
Technical Support: Power
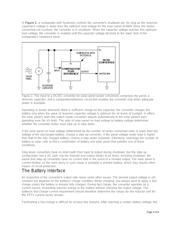
As a power source, the sun offers some impressive advantages over typical battery cells: It generates
virtually limitless energy, requires no recharging, and is expected to last for another five billion years or
so. Today's more efficient, less expensive solar cells provide a practical means of converting the sun's
power into electricity to run our gadgets and gismos (see the appendix, From Photons to Electrons). The
only clouds in this otherwise sunny picture are . . . well, clouds. Because they often obscure the sun, it's
tough to design a system that can reliably provide power.
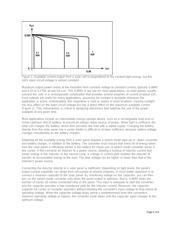
The output current for typical monocrystalline-silicon solar cells directly depends on the amount of
incident sunlight (Figure 1). For example, a typical hobby-grade credit-card-sized silicon cell has an
open-circuit voltage of 0.55V. Internal resistance causes a voltage drop as you draw current from the
cell; but, as light energy drops below the level necessary to support the output load, the cell current-
limits at an almost constant voltage. For a light level of one full sun (solar irradiance of 1kW/m²), the cell
provides a typical short-circuit current of 0.3A.
Page 1 of 8