herunterladen

Freescale Semiconductor
Document Number: AN4705
Application Note Rev. 0, 03/2013
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., 2013
_______________________________________________________________________
Low-Power Wireless Charger Transmitter
Design Using MC56F8006 DSC
by: Xiang Gao
1 Introduction
Wireless power transmission system transfers
electrical power from transmitter to receiver
without any wire connection. Due to safety,
freedom, reliable, convenient and long life,
wireless charging is popular, and widely used in
everything such as toothbrushes, LED candles,
remote controls, medical equipment, mobile
phones, and other equipment.
This paper describes a Freescale low-power
wireless transmitter solution (TX) compliant to
the “Qi” standard of the Wireless Power
Consortium (WPC), using single-stage full-
bridge resonant inverter topology on Freescale
ultra low cost MC56F8006 DSC device.
This application note focuses on cost-effective,
flexible and high integrated platform to show
significant features of low-power wireless
transmitter such as wide DC input voltage range
of 5–16 V with single power stage, free
positioning with multiple primary coils, simple
and robust communication demodulation circuit,
low-power standby operation, precise
Contents
1 Introduction ..................................................................... 1
2 MC56F8006 DSC Advantages and Features ................... 2
3 Target Control Theory ..................................................... 3
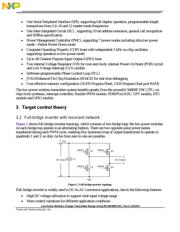
3.1 Full-bridge Inverter with Resonant Network .......... 3
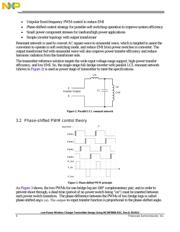
3.2 Phase-Shifted PWM Control Theory ...................... 4
4 System Design Concept ................................................... 5
4.1 System configuration .............................................. 5
4.2 System specification ............................................... 7
5 Hardware Design ............................................................. 7
5.1 MC56F8006 Resource Design ................................ 8
5.2 Power Stage Design ................................................ 9
5.3 Pre-Driver Circuits Design .................................... 14
5.4 Sensing Circuits Design ........................................ 14
5.5 Communication Demodulation Circuits Design ... 14
5.6 Auxiliary Power Supply Design ............................ 15
6 Software Design ............................................................ 16
6.1 System Software Organization .............................. 16
6.2 Main Module Design ............................................ 17
6.3 ISR Design ............................................................ 20
Verzeichnis