EXAR Corporation, 48720 Kato Road, Fremont, CA 94538 · (510) 668-7000 · FAX (510) 668-7017
Visit Exar Web Site at www.exar.com
DATA COMMUNICATIONS APPLICATION NOTE
DAN107
1
Interfacing 16Cxxx UARTs to a CPU
Author: Reinhardt Wagner
Introduction
Due to the variety of CPUs that can be used in conjunction with UARTs, an understanding of a UART‘s CPU
interface is useful. This allows establishing the compatibility of a particular CPU bus and the design for minimal
glue logic as well as optimized bus cycle timing.
UARTs are usually driven by a CPU. EXAR‘s 16Cxxx UART family (16C45x, 16C55x, 16C65x and 16C85x
16C145x, 16C155x, 16C245x, 16C255x series) directly supports the INTEL bus interface. INTEL-derived
CPUs are commonly interfaced to these UARTs despite data-, address- and control-bus timing variations
from CPU type to CPU type.
It is possible to control UARTs by programmable logic, like FPGAs, instead of a CPU or microcontroller. This
also affords a clear understanding of the interface logic.
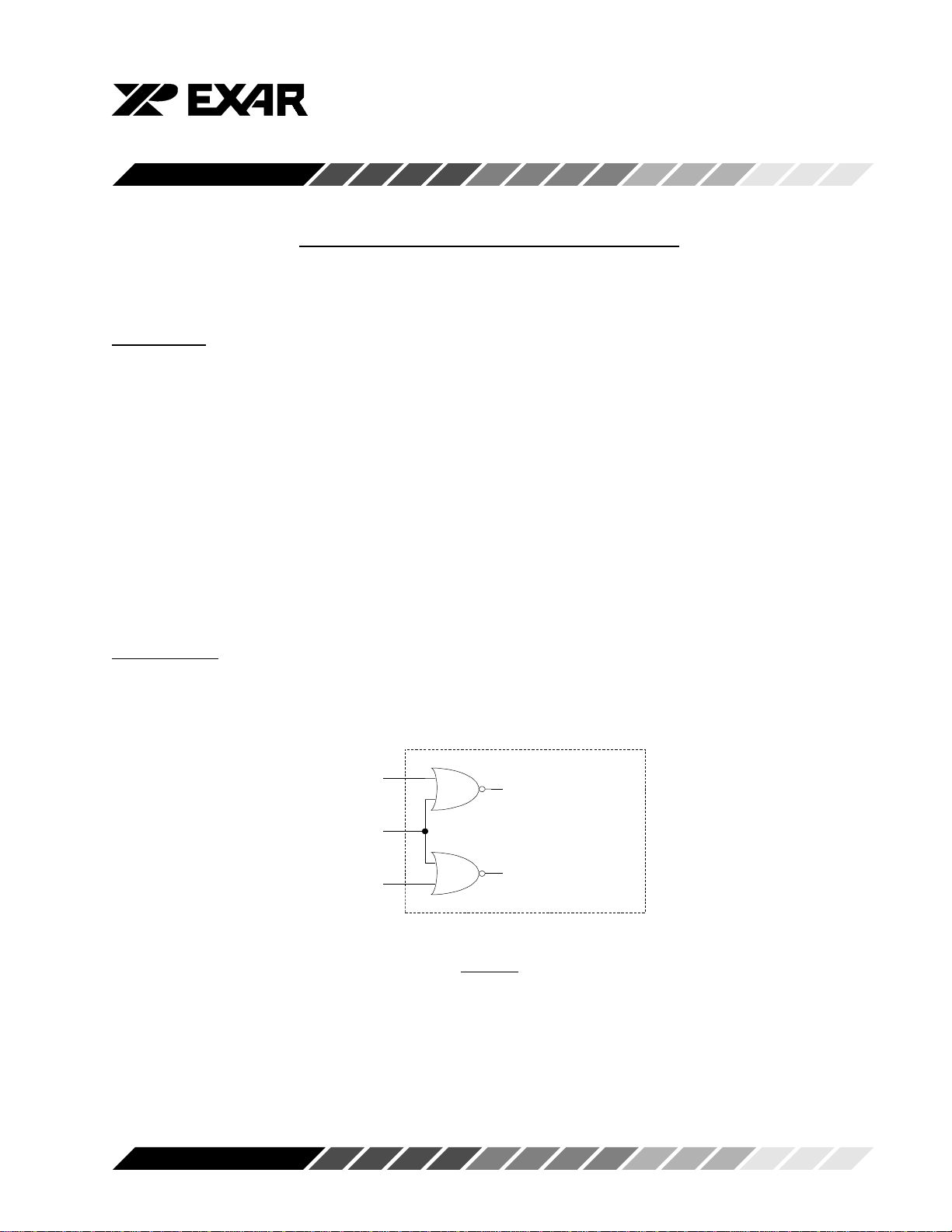
Control Logic
Internal to the 16Cxxx UARTs, the CPU-bus control signals IOR#, IOW# and CS# are logically associated
as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1
Hence the sequence of applying IOR# and CS# during a Read Cycle and IOW# and CS# during a Write
Cycle is unimportant. The following discussion thus refers to the internal UART signals (IOR# +CS#) and
(IOW# + CS#) instead of IOR#, IOW# and CS#.
EXAR Corporation, 48720 Kato Road, Fremont, CA 94538 · (510) 668-7000 · FAX (510) 668-7017
August 1999
IOW#
IOR#
CS#
Internal_Write
Internal_Read
Inside 16Cxxx UART






