herunterladen
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Reference Designs > Hot-Swap and Power Switching Circuits > APP 2765
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Reference Designs > Temperature Sensors and Thermal Management > APP 2765
Keywords: fault protection, temperature, short-circuit, hot swap, fault, thermal, debouncer, hot-swap faults
REFERENCE DESIGN 2765 INCLUDES: Tested Circuit Schematic Description Test Data
Flexible Fault Protection
Dec 29, 2003
Abstract: A flexible circuit is shown that limits current or removes power in response to a command from the
user or other fault-indicating signal. It accommodates manual-reset (MR), over-temperature, and protection in
hot-swap applications. Residing on either the backplane/host side or the removable-card/remote-device side of
the backplane connectors, it guards against start-up faults when a card or board is inserted into a rack or host
with the main power supply turned on.
Many applications require the capability to automatically disconnect power from an operating circuit. Such
applications include thermal shutdown of high-voltage power supplies in radar and X-ray systems, shutdown to
limit inrush current during power-up or hot-swapping of pc cards, and shutdown to ensure that a card is
properly seated before power is applied. In general, a power fault system will keep the power off following the
system fault, until it is deliberately reset.
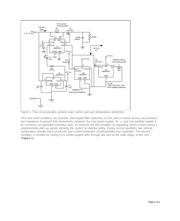
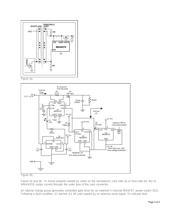
Figure 1 is a flexible circuit that limits current or removes power in response to a command from the user or
other fault-indicating signal. It accommodates manual-reset (MR), over-temperature, and interlock-switch inputs.
U1, for instance, is a circuit-breaker IC designed to offer protection in hot-swap applications. Residing on either
the backplane/host side or the removable-card/remote-device side of the backplane connectors, it guards
against start-up faults when a card or board is inserted into a rack or host with the main power supply turned
on.
Page 1 of 4